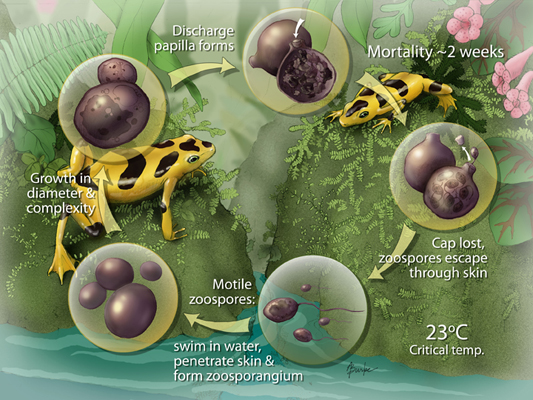
Chytrid fungus, specifically Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis (Bd), is a highly infectious and deadly fungal pathogen that affects amphibians, particularly frogs and toads. It's one of the main drivers of amphibian population declines and extinctions worldwide.
Chytrid fungus spreads through: 1. Direct contact: Infected amphibians can transmit the fungus to others through skin-to-skin contact. 2. Waterborne transmission: The fungus can survive in water and infect amphibians through skin contact with contaminated water. 3. Contaminated environments: The fungus can persist in environments, such as soil, water, and vegetation, allowing it to infect new hosts.
Chytrid fungus causes the disease chytridiomycosis, which can lead to: 1. Skin lesions: The fungus infects the skin, causing lesions and damage to the keratinized skin layers. 2. Electrolyte imbalance: The fungus disrupts the amphibian's ability to regulate electrolytes, leading to cardiac arrest. 3. Death: Infected amphibians often die from cardiac arrest, secondary infections, or other complications.